
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s, is an open-source platform designed to automate the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. It groups containers that make up an application into logical units for easy management and discovery.
Key Components of Kubernetes:
-
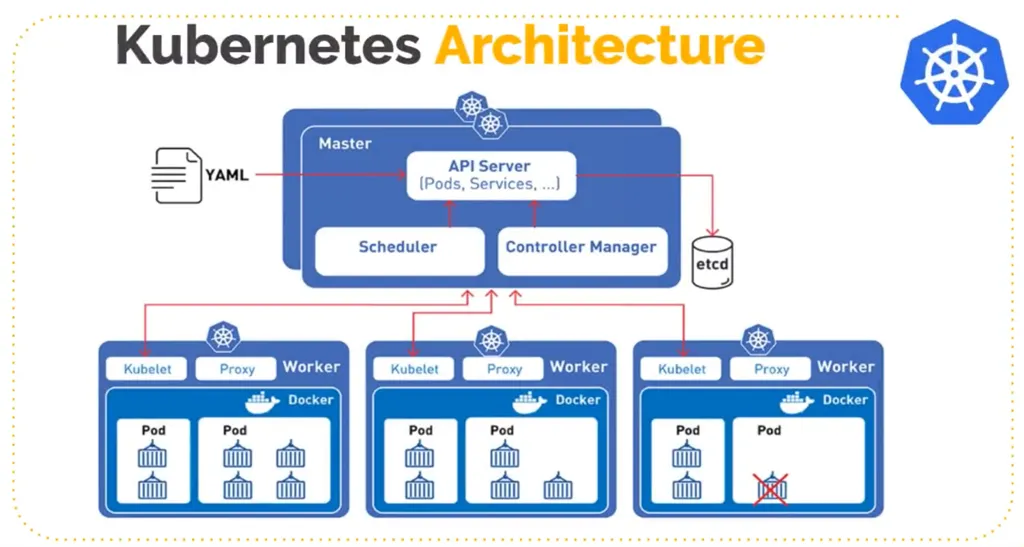
Control Plane: Manages the Kubernetes cluster, maintaining the desired state of applications and performing tasks such as scheduling and scaling.
- API Server: Serves as the front end of the Kubernetes control plane, handling internal and external requests.
- etcd: A consistent and highly available key-value store used as Kubernetes’ backing store for all cluster data.
- Controller Manager: Runs controller processes that regulate the state of the cluster.
- Scheduler: Assigns workloads to nodes based on resource availability.
-
Nodes: Machines (virtual or physical) that run containerized applications. Each node contains:
- Kubelet: An agent that ensures containers are running in a Pod.
- Kube-proxy: Maintains network rules on nodes, allowing communication to your Pods.
- Container Runtime: Software responsible for running containers, such as Docker or containerd.
Benefits of Using Kubernetes:
- Portability: Operates across various environments, including on-premises, public, or hybrid clouds.
- Scalability: Automatically scales applications up or down based on demand.
- High Availability: Ensures applications are always running and accessible.
- Resource Optimization: Efficiently manages resources, optimizing hardware usage.
Getting Started with Kubernetes:
-
Installation: Set up a Kubernetes cluster using tools like Minikube for local development or managed services like Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) for production environments.
-
Deploying Applications: Define your application using YAML files, specifying the desired state, and apply them to your cluster.
-
Managing Applications: Use
kubectl, the command-line tool for Kubernetes, to interact with your cluster, manage applications, and monitor their status.
For comprehensive tutorials and documentation, refer to the Kubernetes Documentation.
By leveraging Kubernetes, organizations can achieve a robust and flexible platform for managing containerized applications, facilitating rapid development and deployment cycles.